Page History
Contents
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Child pages
| Children Display |
|---|
Introduction
Alternative splicing (AS) is an important process of gene regulation at transcriptional level and substantially contributes to the understanding of proteomic diversity and function. In order to advance in large-scale research about the functional impact of AS on the proteome, automated methods are required for identifying AS events and linking them to functional regions of proteins in a systematic manner.
AstaFunk is a JAVA tool to study how diversity of a custom transcriptome translates into functional variation, based on standard transcriptome annotations and protein family profiles. In a nutshell, ASTAFUNK translates alternatively spliced parts of open reading frames (given by GTF annotation) on the fly into amino acid sequences. Subsequently, profile HMMs of Pfam database are searched against these amino acid sequences only in the regions of alternative splicing events. ASTAFUNK algorithm is designed to avoid redundant sequence scans in AS-enriched transcriptomes.
This document presents the information to download binaries, build AstaFunk from source code and execute basic commands.
Obtaining AstaFunk
Source Codessource code
Alternatively, the current version can always be obtained from the GIT repository. Clone the Git repository of the barna. The Barna library consists of a set of tools bundled with the package.
| Code Block |
|---|
$> git clone http://bitbucket.sammeth.net/bitbucket/scm/barna/barna.git Cloning into 'barna'... remote: Counting objects: 29522, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (11638/11638), done. remote: Total 29522 (delta 11254), reused 27997 (delta 10681) Receiving objects: 100% (29522/29522), 99.43 MiB | 706.00 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (11254/11254), done. Checking connectivity... done. $> git checkout vitorafunk_dev_fix1stable Branch vitorafunk_dev_fix1stable set up to track remote branch vitorastafunk_dev_fix1stable from origin. Switched to a new branch 'vitorafunk_dev_fix1stable' |
Building binaries
Build the binaries of AStalavista and create a distribution version.
| Code Block |
|---|
$> cd barna/
$> cd barna.astalavista/
$> ../gradlew dist
.
. {some log messages}
.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 2 mins 11.574 secs |
Extracting binary files
Enter into the distribution directory and extract the files (.tgz or .zip). In barna.astalavista directory:
| Code Block |
|---|
$> cd build/distributions/ $> unzip astalavista-34.20.1-SNAPSHOT.zip |
Check build
The current bundle uses 'astalavista' as the default tool. You can switch tools with the -t option and get help for a specific tool with -t <toolname> --help. This will print the usage and description of the specified tool
| Code Block |
|---|
$> ./astalavista -t astafunk --help |
You You will see:
| Code Block |
|---|
$> ./astalavista -t astafunk --help [INFO] Astalavista v4.0 (Flux Library: 1.30) -------Documentation & Issue Tracker------- Barna Wiki (Docs): http://confluence.sammeth.net/confluence Barna JIRA (Bugs): http://jira.sammeth.net/jira Please feel free to create an account in the public JIRA and reports any bugs or feature requests. ------------------------------------------- Current tool: astafunk Search HMM-profiles of protein families (Pfam) on alternatively spliced genes. Tool specific options: . . {help messages} . |
Input data
In this section, we describe the optional and mandatory input data required to run AstaFunk:
--hmm <HMM_FILE.hmm>
<HMM_FILE> is an unique profile HMM or multiples HMMs in the same file (with extension .hmm) of the Pfam-A database from Pfam. You can download the complete Pfam-A database from FTP site: ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/Pfam/current_release/Pfam-A.hmm.gz or download individual profiles using the family browser: http://pfam.xfam.org/family/browse.
--gtf <GTF_FILE.gtf>
<GTF> is the gene annotation based on GTF (Gene Transfer Format) format file of the input genome.
If you only have a GFF annotation file, convert to GTF using gffread of Cufflinks or other script.
--genome <GENOME_DIR>
<GENOME_DIR> is the directory path to FASTA files (one chromosome per file) of the genome assembly.
| Warning | ||
|---|---|---|
Assume your annotation GTF file is (some fields are hidden after coordinates):
So, the FASTA files in the directory <GENOME_DIR> must be chr1.fasta, chr2.fasta, chr3.fasta, chr4.fasta and chr5.fasta. |
-r|--reference <REFERENCE_FILE>
Reference file with predicted domains for the reference transcript of each alternatively spliced gene.
How to Create a Reference File
<REFERENCE_FILE> is computed by hmmsearch of the HMMER program, using the command line below:
| Code Block |
|---|
$> hmmsearch --cut_ga --domtblout <REFERENCE_FILE> Pfam-A.hmm <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta> |
hmmsearch is the HMMER algorithm (hmmer.org) to search one or more profiles (from the Pfam-A.hmm database) against the amino acid sequences of reference transcripts (in the <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS>.fasta, see help below). The parameter --cut_ga is that hmmsearch uses gathering domain thresholds stored in the HMM profiles during predictions. The --domtblout output saves a parseable table of per-domain hits to <REFERENCE_FILE>. The reference transcript is the transcript with the longest ORF of a gene.
Using AstaFunk to Generate a Multi-fasta File with the Reference Transcripts
AstaFunk includes a feature to generate a multi-fasta file with the amino acid sequences of reference transcripts for a given annotation.
Firstly, you execute ASTAFUNK to print on standard output (redirected to the file <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta>) the amino acid sequences of the reference transcripts. A reference transcript is the transcript with the longest Open Reading Frame (ORF) of an alternatively spliced gene.
Obtain the reference transcript FASTA file with the command:
| Code Block |
|---|
$> astalavista -t astafunk --tref --genome <GENOME_DIR> --gtf <GTF_FILE.gtf> > <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta> |
Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| [--hmm <HMM_FILE>] | Profile-HMM file. |
| [--gtf <GTF>] | Gene annotation (GTF) |
| [--genome <GENOME>] | Path to the directory with the genomic sequences, i.e., one fasta file per chromosome/scaffold/contig with a file name corresponding to the identifiers of the first column in the GTF annotation |
| [(-r|--reference) <REFERENCE_FILE>] | Path to the reference domain file. See 3.4.1 - Getting Started |
| [-e|--exh] | Perform exhaustive search against HMM database (default: heuristic search) - |
| [-g|--output-hits-per-gene] | Output best non-overlapped domain hits of the AS gene. (Default: output best non-overlapped domain hits of each variant). |
| [--all] | Output all different overlapped domain hits of each variant. (Default). |
| [-l|--local] | Run local search mode. (Default: glocal) |
| [(-o|--overlapping) <OVERLAPPING>] | Hit overlapping threshold (integer) (default: 0) |
| [--tref] | Print on standard output the sequences of reference transcript of each gene on FASTA format. This parameter is only used with--gtf and --genome parameters. |
| [--const] | Performs a domain search only on constitutive regions of all genes. |
| [--naive] | Run Näive search. Search domains against all genes with alternative splicing without merging events and search space reduction heuristics. Needs a reference domain file (Method to obtain results for the paper). |
| [--test] | Search HMM database (--hmm) against FASTA sequences. (Method to obtain results for the paper). |
| [--fa <SEQUENCE_FILE>] | Path to FASTA Sequence file. This file is used as input to evaluate the method employed by AstaFunk to align sequences (--test). |
| [--cpu <CPU>] | Number of threads (Default: 1) |
| [--verbose] | Verbose. |
Input data
In this section, we describe the optional and mandatory input data required to run AstaFunk:
--hmm <HMM_FILE.hmm>
<HMM_FILE> is an unique profile HMM or multiples HMMs in the same file (with extension .hmm) of the Pfam-A database. You can either download the complete Pfam-A database from the EBI FTP site or specific Pfam profiles using the Pfam family browser.
--gtf <GTF_FILE.gtf>
<GTF> is the gene annotation based on GTF (Gene Transfer Format) format file of the input genome.
If you only have a GFF annotation file, convert to GTF using gffread of Cufflinks or other script.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
The GTF file must be pre-processed to guarantee that AStalavista extracts only events that affect CDS regions. For while, this is step is necessary but we are working to increment the tool to automatically use the CDS coordinates to construct the AS events.
|
--genome <GENOME_DIR>
<GENOME_DIR> is the directory path to FASTA files (one chromosome per file) of the genome assembly.
| Warning | ||
|---|---|---|
Assume your annotation GTF file is (some fields are hidden after coordinates):
So, the FASTA files in the directory <GENOME_DIR> must be chr1.fasta, chr2.fasta, chr3.fasta, chr4.fasta and chr5.fasta. |
-r|--reference <REFERENCE_FILE>
Reference domain file with predicted domains for the reference transcript of each alternatively spliced gene. See below how to create a reference domain file.
Reference Domain file
<REFERENCE_FILE> is computed by hmmsearch of the HMMER program, using the command line below:
| Code Block |
|---|
$> hmmsearch --cut_ga --domtblout <REFERENCE_FILE> <HMM_FILE> <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta> |
hmmsearch is the HMMER algorithm (hmmer.org) to search one or more profiles (from the Pfam-A.hmm database) against the amino acid sequences of reference transcripts (in the <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS>.fasta, see help below). The parameter --cut_ga is that hmmsearch uses gathering domain thresholds stored in the HMM profiles during predictions. The --domtblout output saves a parseable table of per-domain hits to <REFERENCE_FILE>. The reference transcript is the transcript with the longest ORF of a gene. See below how to obtain the reference transcript FASTA file <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta>.
Reference transcript sequences <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta>
AstaFunk includes a feature to generate a multi-fasta file with the amino acid sequences of reference transcripts for a given annotation. Firstly, you execute ASTAFUNK to print on standard output (redirected to the file <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta>) the amino acid sequences of the reference transcripts. A reference transcript is the transcript with the longest Open Reading Frame (ORF) of an alternatively spliced gene.
| Code Block |
|---|
$> astalavista -t astafunk --tref --genome <GENOME_DIR> --gtf <GTF_FILE.gtf> > <REFERENCE_TRANSCRIPTS.fasta> |
Program Output
AstaFunk
Program Usage
The basic search command of AstaFunk is:
| Code Block |
|---|
$> astalavista -t astafunk --gtf <GTF_FILE.gtf> --genome <GENOME_DIR> --hmm <HMM_FILE.hmm> --reference <REFERENCE_FILE> |
Options
[--hmm <HMM_FILE.hmm>] | Path to the profile HMM file |
[--genome <GENOME>] | Path to the directory with the genomic sequences, i.e., one fasta file per chromosome/scaffold/contig with a file name corresponding to the identifiers of the first column in the GTF annotation |
[--gtf <GTF_FILE.gtf>] | Path to the GTF reference annotation |
[(-r|--reference) <REFERENCE_FILE>] | Path to the reference domain file |
[--tref]
| Print to standard output the FASTA sequences of non-AS transcripts and reference transcripts (longest ORF) of AS genes. This parameter is only used with--gtf and --genome parameters |
[-g|--output-hits-per-gene] | Output best non-overlapped domain hits of the alternatively spliced (AS) gene.(Default: output best non-overlapped domain hits of each variant; Method to obtain results for the paper). |
[(-o|--overlapping) <OVERLAPPING>] | Hit overlapping allowed [0.0 to 1.0] (default: 0) |
[-l|--local] | Run local search (Default: glocal) |
[--all] | Output the all domain hits of each alternative variant.(Default: output best non-overlapped domain hits of each variant). |
[-e|--exh] | Perform exhaustive search against HMM database. |
[--naive] | Run Näive search. Search domains against all genes with alternaive splicing. This search uses a reference file (Method to obtain results for the paper). |
[–const] | Performs a domain search only on constitutive regions of all genes (Method to obtain results for the paper) |
[--cpu <CPU>] | Number of threads to run (Default: 1) |
[--verbose] | Verbose |
Program Output
AstaFunk prints on standard output the predictions of domains for each variant. See below column names of the standard output (tab-separated):
chr1. chr: Field "seqname" of the GTF annotation; name of the chromosome or scaffold; Example: “chr1”.
gene2. loci_cluster
_name: string of concatenated AS transcript/gene identifiers clustered in the same loci. Example:
“uc001dhm“uc001dhm.2,uc001dhn.3,uc001dho.3”.
3
”.
namedomain_
hmm: Name of the protein family in the profile HMM. Example: “ADK”.acc: Accession number of the profile HMM. Example: “PF00406.19”.
description: Description of the profile HMM. Example: “Adenylate kinase”.
bitscore: Bit score of the alignment
start_seq, end_seq: Start/End position of the alignment in the sequence.
start_genomic, end_genomic: Start/End position of the alignment in the genome
first_source, last_source: Source is the start genomic position of the merged AS events. Sink is the end genomic position of the merged AS events.
start_model, end_model: Alignment start/end state number of the profile HMM
length_model: number of states of the profile HMM
sequence: Sequence ID of the gene/transcript used to search the protein domain/family. This sequence is randomly selected from the variants
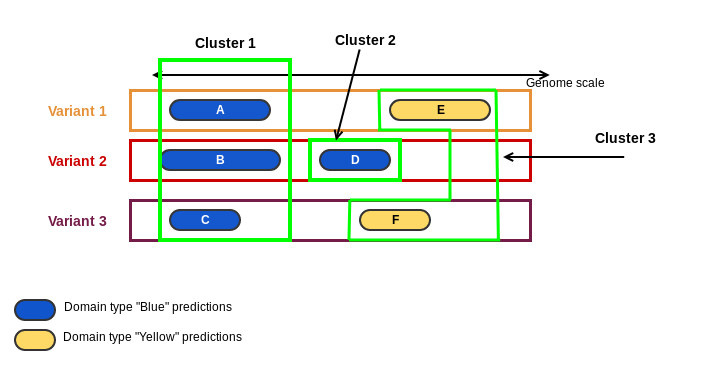
cluster: a loci cluster has one or more domain clusters. Domain clusters are predictions of the same domain that overlap by genomic coordinates. It is integer number. In the cartoon below, domains "Blue" and "Yellow" were predicted on 3 variants of a loci. Predictions A, B and C are predictions of the same domain and they are overlapping by their genomic coordinates, resulting in the Cluster 1. Prediction D of domain "Blue" is overlapping the prediction F, but prediction F is from another domain "Yellow". It results in the Cluster 2. Finally, predictions E and F are from domain "Yellow" and they are overlapping the same genomic region, forming the Cluster 3.
4. merged_variant: set of transcripts with same exon/intron composition between the first source and last sink. If variants contains a list of transcripts identifiers separated by commas means that the transcripts have the same exon/intron composition between the first source and last sink.
Getting Started
Searching protein domains on alternatively spliced regions of human gene TNNT1
According to RefSeq (NM_003283),
This gene encodes a protein that is a subunit of troponin, which is a regulatory complex located on the thin filament of the sarcomere. This complex regulates striated muscle contraction in response to fluctuations in intracellular calcium concentration.
Input
Command line
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$> astalavista -t astafunk --tref --gtf tnnt1.gtf --genome ~/example/genome/ > reference_tx.fasta |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$> hmmsearch --domtblout reference_file ~/Databases/Pfam/Pfam-A.hmm reference_tx.fasta |
| Tip | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
or skip these commands and use directly the whole database Pfam-A.hmm as parameter for the option [–hmm]. |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
astalavista -t astafunk --genome ~/example/genome/ --gtf tnnt1.gtf --reference reference_file --hmm database.hmm |
Extra: Constitutive Domains
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
astalavista -t astafunk --const --genome ~/example/genome/ --gtf tnnt1.gtf --reference reference_file --hmm database.hmm |
Output
AstaFunk identifies six complete alternative events between the eight alternative transcripts of the gene TNNT1 (in the paper we present, just for an example, only two events). See the standard output:
| # | chr | gene_cluster_name | name_hmm | acc | description | bitscore | start_seq | end_seq | start_genomic | end_genomic | first_source | last_sink | start_model | end_model | length_model | sequence | variants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 35.2309670601 | 1 | 102 | -55147129 | -55134152 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000588426.5 | ENST00000588426.5 |
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 98.6465479489 | 85 | 205 | -55141239 | -55134200 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000588981.5 | ENST00000588981.5 |
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 139.0575466987 | 1 | 135 | -55141281 | -55134152 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000587465.6 | ENST00000587465.6 |
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 139.0575466987 | 1 | 135 | -55141281 | -55134152 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000585321.6 | ENST00000585321.6 |
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 139.0575466987 | 1 | 135 | -55141281 | -55134152 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000536926.5 | ENST00000536926.5 |
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 158.3576407894 | 69 | 205 | -55141287 | -55134152 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000291901.12 | ENST00000291901.12 |
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 158.3576407894 | 58 | 194 | -55141287 | -55134152 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000356783.9 | ENST00000356783.9 |
| EHIT | chr19 | ENST00000291901.12,ENST00000356783.9,ENST00000587465.6, ENST00000587758.5,ENST00000585321.6,ENST00000588981.5, ENST00000536926.5,ENST00000588426.5 | Troponin | PF00992.17 | Troponin | 158.3576407894 | 58 | 194 | -55141287 | -55134152 | -55147168 | -55147168 | 1 | 134 | 134 | ENST00000587758.5 | ENST00000587758.5 |
When different variants resulting in predictions with same domain, score, and genomic coordinates, these predictions are collapsed in a unique prediction. In this case, the variants collapsed are separated by semi-colons (";");
5. acc: Accession number of the profile HMM. Example: “PF00406.19”. Other possible values for this field:
- <ACC_NUMBER>-NO_CDS: AStalavista in silico translation was not performed because the transcript does not have a valid CDS: CDS sequence is not multiple of three or it has a in-frame stop codon.
- <ACC_NUMBER>-NO_HIT: it was expected a domain <ACC_NUMBER>, but it was not predicted in the alternative splicing event region.
6. bitscore: Bit score of the alignment.
7. start_seq: Start position of the alignment in the sequence. This field can be a semi-colon-separated list of start positions, indicating that another prediction with the same domain, score and genomic coordinates was collapsed in this prediction.
8. end_seq: End position of the alignment in the sequence. This field can be a semi-colon-separated list of end positions, indicating that another prediction with the same domain, score and genomic coordinates was collapsed in this prediction.
9. start_genomic : Start position of the alignment in the genome
10. end_genomic: End position of the alignment in the genome
11. first_source : Source is the start genomic position of the fused AS events.
12. last_sink: Sink is the end genomic position of the fused AS events.
13. start_model: Alignment start state of the profile HMM.
14. end_model: Alignment end state of the profile HMM
15. length_model: number of states of the profile HMM
16. event code: code of events overlapped by the domain prediction. The pipes "|" separate the codes of multiple events. This field can be a semi-colon-separated list, indicating that another prediction with the same domain, score and genomic coordinates was collapsed in this prediction.
17. splice chain: splice chain of events overlapped by the domain prediction. The pipes "|" separate the splice chains of multiple events. This field can be a semi-colon-separated list, indicating that another prediction with the same domain, score and genomic coordinates was collapsed in this prediction.
18. variant list: variant list of events overlapped by the domain prediction. Different variants of the same event are enclosed by brackets, e.g., [tx1][tx2, tx3] are two variant of a event e where the 1st variant is represented by tx1 and the 2nd variant is represented by tx2 and tx3. This field can be a semi-colon-separated list, indicating that another prediction with the same domain, score and genomic coordinates was collapsed in this prediction. The pipes "|" separate the variant list of multiple events:
| Tip | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Example of reporting multiples overlapped events by a AS domain prediction:
Example of reporting domain predictions when two or more predictions were collapsed due they have the same domain, score and genomic coordinates:
will be reported as:
|
To learn more about AS event patterns see references on 3.1 - Tool ASTA (AS Event Retriever).
Mode Summary
The parameters without brackets are mandatory for the respective mode. Otherwise, it is optional. Parameters between pipe ("|") are mutually exclusive.
Search Alternatively Spliced Domains
Search Pfam protein domains on alternatively spliced regions of the variants. This mode uses a series of heuristics to avoid redundant scans on AS-enriched transcriptomes.
| Code Block |
|---|
astalavista -t astafunk [--verbose] [--cpu <INT>] [--all | -g] [--local] [-o <INT>] --genome <GENOME_DIR> --gtf <GTF_FILE> --hmm <HMM_FILE> --reference|-r <REFERENCE_FILE> |
The parameter --all will report all prediction of different domains (even they are overlapping in genomic coordinates) of each variant of an AS gene. The parameter -g will report the best domain hits (non-overlapping in genomic coordinates) among all variants of a gene, i. e. it will report the best non-overlapped domain predictions of an AS gene. The default reporting is best non-overlapped domain prediction of each variant of an AS gene.
Search Constitutive Domains
Search constitutive domains, i. e. report the domain hits found on constitutive exons. On AS genes, AstaFunk searches domains only on the sequence of the reference transcript, i. e. the transcript with the longest ORF. Otherwhise, AstaFunk reports all domain hits of the non-AS genes.
| Code Block |
|---|
astalavista -t astafunk [--verbose] [--cpu <INT>] [--local] [-o <INT>] --const --genome <GENOME_DIR> --gtf <GTF_FILE> --hmm <HMM_FILE> --reference|-r <REFERENCE_FILE> |
Search AS domains exhaustively
Searches exhaustively, i. e., without a reference domain file, the HMM database against the variant sequences.
| Code Block |
|---|
astalavista -t astafunk [--verbose] [--cpu <INT>] [--all | -g] [--local] [-o <INT>] -e|--exh --genome <GENOME_DIR> --gtf <GTF_FILE> --hmm <HMM_FILE> |
Näive Search
Search the HMM database against each transcript of an AS gene. Differently from "Search Alternatively Spliced Domains" mode, this mode searches the entire sequence of all transcripts, potentially resulting in redundant searches on the AS-enriched transcriptomes and constitutive regions of the transcripts.
| Code Block |
|---|
astalavista -t astafunk [--verbose] [--cpu <INT>] [--local] [-o <INT>] --naive --genome <GENOME_DIR> --gtf <GTF_FILE> --hmm <HMM_FILE> --reference|-r <REFERENCE_FILE> |
Print the reference transcript sequences
Print on standard output the FASTA sequences of (reference) transcripts of (AS-)genes on <GTF_FILE>.
| Code Block |
|---|
astalavista -t astafunk --tref --genome <GENOME_DIR> --gtf <GTF_FILE> |
Search HMM database against FASTA sequences
Mode to search a HMM database against a FASTA sequence file.
| Code Block |
|---|
astalavista -t astafunk [--local] [-o <INT>]--test --hmm <HMM_FILE> --fa <SEQUENCE_FILE> |